Keywords AI
Cursor and Claude Code are AI coding assistants that think, edit files, run shell commands, and call tools on your behalf. But you have no visibility into what they're doing. Every thinking block, tool call, and file edit happens without any way to inspect it.
This guide covers how to set up hooks that capture agent activity and send hierarchical traces to Keywords AI.

Table of Contents
- Why You Need Observability for Cursor and Claude Code
- What Are Hooks in AI Code Assistants
- Cursor Agent Tracing Setup
- Claude Code Hooks Setup
- What Data Gets Captured
- How to Debug with Agent Traces
- Claude Code vs Cursor Comparison
Why You Need Observability for Cursor and Claude Code
When you use Cursor or Claude Code, the agent:
- Thinks through the problem (reasoning blocks)
- Reads your files
- Edits code
- Runs shell commands
- Calls MCP tools
Without observability, you can't answer basic questions:
- Why did the agent make that change?
- What files did it read?
- How long did each step take?
- Did it fail silently?
With Keywords AI, every agent turn becomes a hierarchical trace:
cursor_abc123_xyz789 (38.9s) ├── Thinking 1 (0.5s) - "Let me analyze the code..." ├── Thinking 2 (0.3s) - "I should update the function..." ├── Edit: utils.py (0.1s) ├── Shell: npm test (4.1s) ├── MCP: list_logs (0.8s) └── Thinking 3 (0.2s) - "Tests passed, done."
Now you can see exactly what happened in each agent turn.
What Are Hooks in AI Code Assistants
Both Cursor and Claude Code provide hooks, which are extension points that fire during agent execution:
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| Before prompt | User submits a message |
| After thinking | Agent produces a reasoning block |
| After tool call | Agent uses a tool (file, shell, MCP) |
| After response | Agent completes its turn |
| Stop | Agent stops (user cancels or completion) |
Our integration uses these hooks to capture events in real-time and send them to Keywords AI as structured traces.
The mental model:
Agent Event → Hook Fires → Python Script → Keywords AI API
Cursor Agent Tracing Setup
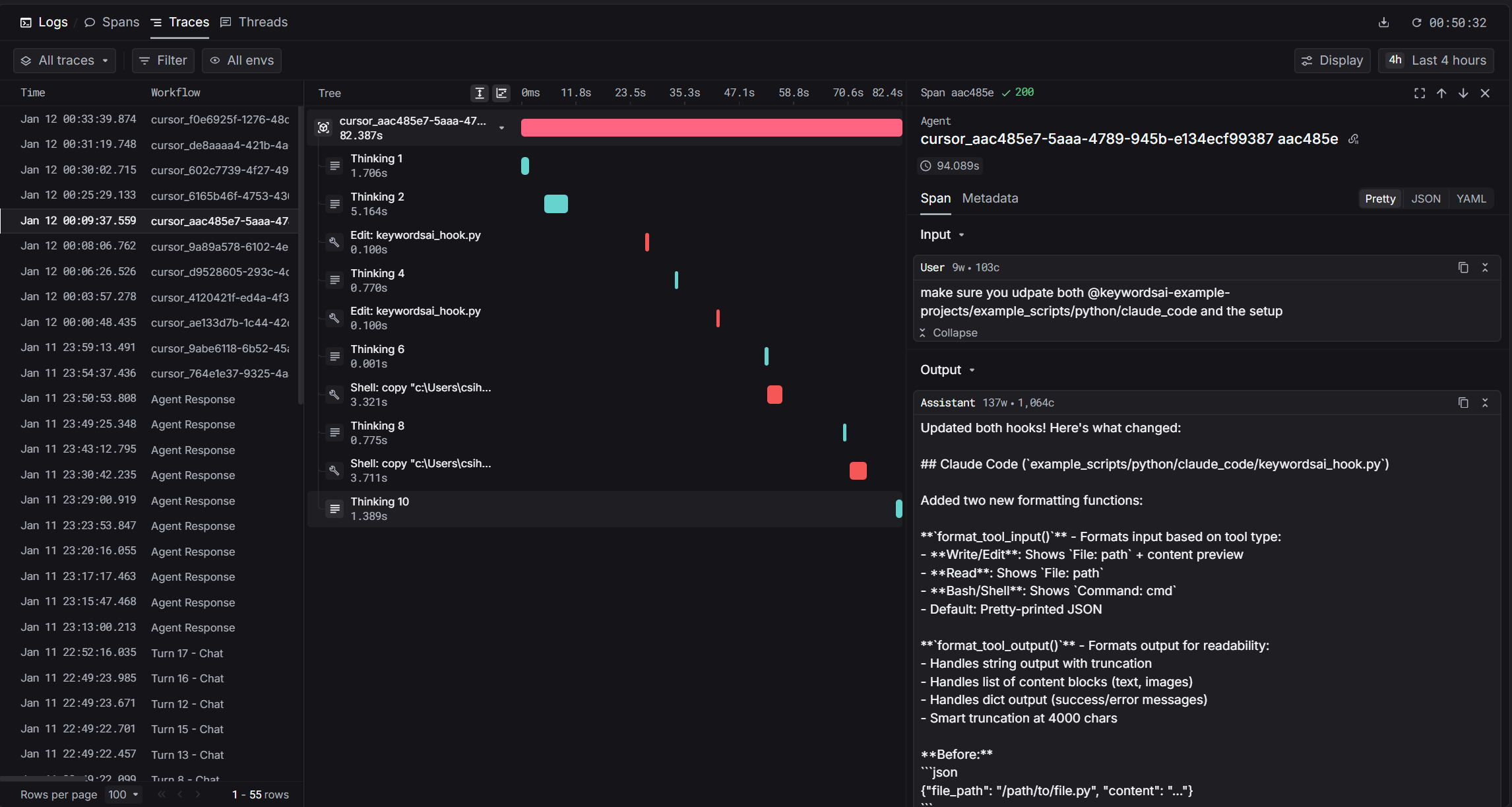
Cursor provides rich hooks that fire during agent execution. The architecture captures events as they happen:
Cursor Agent Hooks Reference
| Hook | Trigger | Data Captured |
|---|---|---|
beforeSubmitPrompt | User sends prompt | User input, start time |
afterAgentThought | Agent produces thinking | Thinking text, duration |
afterShellExecution | Shell command completes | Command, output, exit code |
afterFileEdit | File edited | File path, edits, diff |
afterMCPExecution | MCP tool completes | Tool name, input, output |
afterAgentResponse | Agent responds | Response text (creates root span) |
Cursor hooks fire in real-time. Each event arrives as it happens, so you get streaming observability into agent behavior.
Quick Setup
Setting up Cursor observability takes just 3 steps:
- Set environment variables (
KEYWORDSAI_API_KEY,TRACE_TO_KEYWORDSAI) - Download the hook script to
~/.cursor/hooks/ - Configure hooks.json with all hook events
Claude Code Hooks Setup
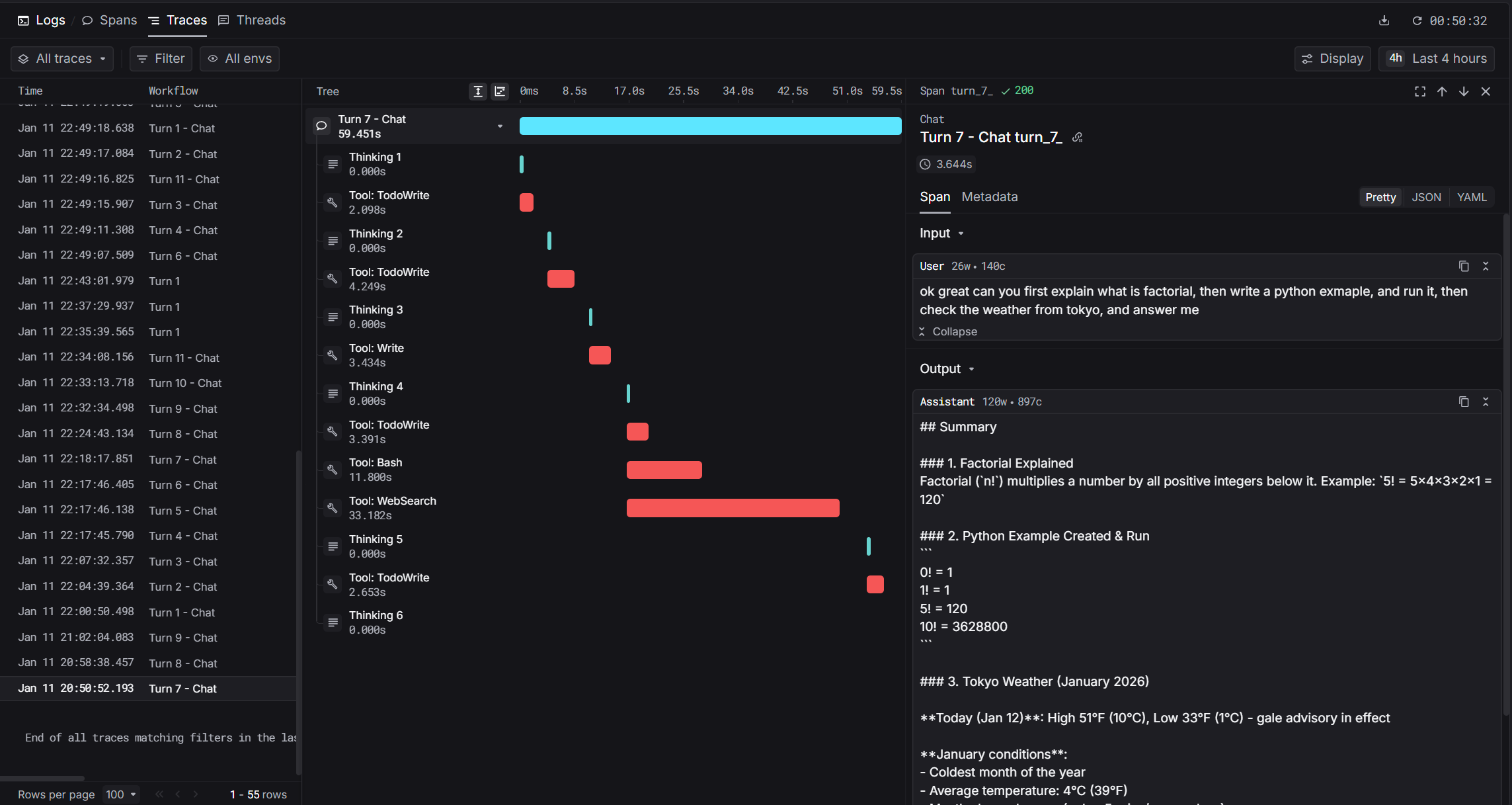
Claude Code takes a different approach. Instead of real-time hooks, it stores conversation transcripts as JSONL files. The hook fires after the agent response completes:
How Claude Code Hooks Work
Claude Code uses a Stop hook that triggers after each agent turn. The hook script:
- Locates the active transcript file
- Reads new messages since last processing
- Parses thinking blocks, tool calls, and responses
- Builds hierarchical spans
- Sends to Keywords AI
This post-hoc approach means Claude Code captures richer metadata (like token counts) that aren't available during streaming.
Quick Setup
Setting up Claude Code observability takes just 3 steps:
- Set environment variables (
KEYWORDSAI_API_KEY,TRACE_TO_KEYWORDSAI) - Download the hook script to
~/.claude/hooks/ - Configure settings.json with the Stop hook
👉 Full Claude Code Setup Guide →
What Data Gets Captured
Both integrations capture rich observability data and organize them as hierarchical spans:
Span Types
| Span | log_type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Root | agent | The complete agent turn |
| Thinking | generation | Reasoning blocks |
| Tool | tool | File/shell/MCP invocations |
Common Data
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| User prompt | What you asked the agent |
| Assistant response | The agent's final response |
| Thinking blocks | Reasoning/planning content |
| Tool calls | File reads, writes, shell commands, MCP tools |
| Timing | Start time, end time, duration per span |
Claude Code Bonus: Token Usage
Claude Code captures additional metrics not available in Cursor:
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| Token usage | Prompt tokens, completion tokens, cache tokens |
| Model name | Which model was used (e.g., claude-sonnet-4-20250514) |
| Cache info | Cache creation and read tokens |
How to Debug with Agent Traces
Example workflows:
"Why did the agent take so long?"
- Open the trace in Keywords AI
- Look at the span timeline
- Find the longest-running span
- Investigate: Was it a slow shell command? A large file read? An MCP timeout?
"The agent made the wrong edit"
- Find the trace for that turn
- Read the thinking spans leading up to the edit
- See what context the agent had (what files it read)
- Identify where its reasoning went wrong
"Compare two approaches"
When you ask the agent to solve a problem differently:
- Pull traces for both attempts
- Compare thinking patterns
- Compare tool usage (did one read more files?)
- Compare durations (which was faster?)
"Track agent behavior over time"
- Are turns getting faster or slower?
- Is the agent using more or fewer tool calls?
- Are certain tools failing more often?
Claude Code vs Cursor Comparison
| Feature | Cursor | Claude Code |
|---|---|---|
| Hook type | Multiple real-time hooks | Single Stop hook |
| Data source | JSON via stdin | JSONL transcript files |
| Timing | Real-time (as events happen) | Post-hoc (after response) |
| Token usage | Not available | Full usage details |
| Cache info | Not available | Cache creation/read tokens |
| MCP support | Yes | Yes |
Both tools give you full observability into agent behavior. The main difference is that Claude Code also captures token usage, which is useful for cost tracking.
Get Started
With Keywords AI hooks, you get:
- Every thinking block the agent produces
- Every tool call with inputs and outputs
- Duration for each span
- Token usage (Claude Code only)
Setup takes about 5 minutes.
- Get your Keywords AI API key
- Follow the setup guide:


